When talking about electric vehicles (EV) we rarely think of hydrogen fuel cell cars. After all, the market is dominated by battery-powered electric vehicles (BEVs) and hybrid vehicles. While hydrogen cars are seen as just as environmentally friendly as a regular BEV, they somehow flew under the radar of manufacturers and consumers.
So why don’t hydrogen cars get more love and will we ever adopt hydrogen cars in Malaysia? Let’s find out below.
| Table of Contents |
How Do Hydrogen Fuel Cell Cars Work?
Hydrogen fuel cell cars are a type of fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) as they use hydrogen fuel cells to power their electric motors. They are largely similar to a BEV except that they run on a different power source.
In a hydrogen car, compressed hydrogen gas from the gas tank is sent to the fuel cell stack where the gas goes through reverse electrolysis and combines with oxygen from the atmosphere. This process produces electrical energy and clean water. The electrical energy is then sent to the motor which drives the wheels and moves the car. The water, on the other hand, is sent to the exhaust pipe where it’s expelled from the car.
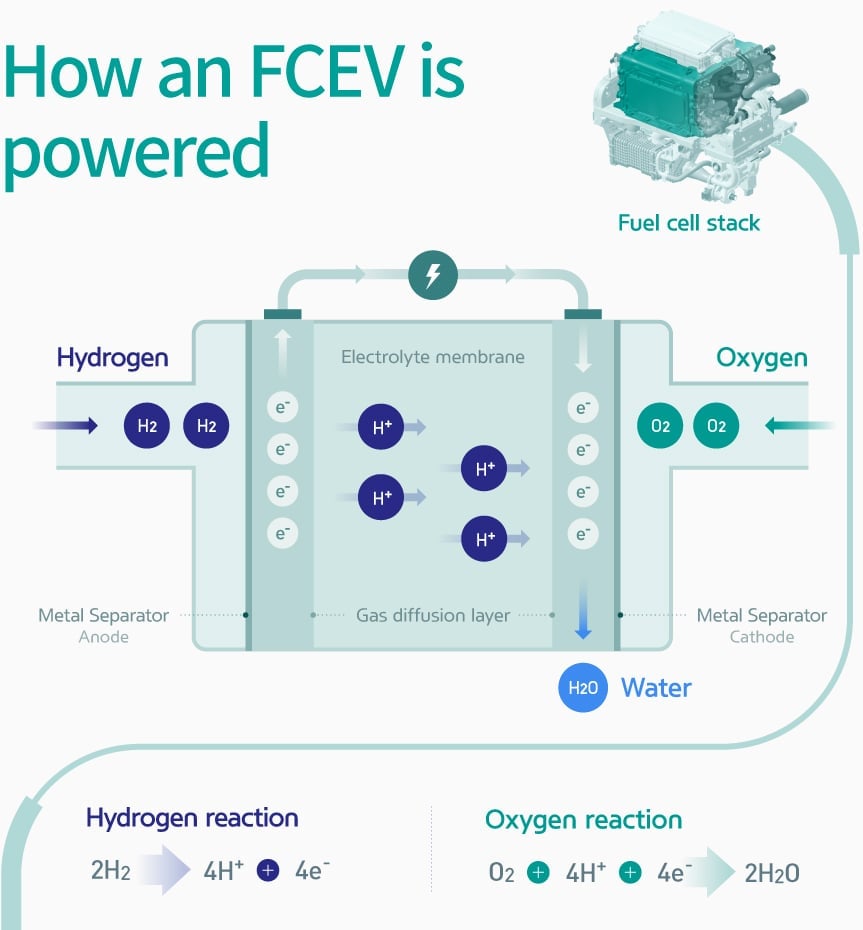
Image source: Hyundai
What Happens in the Hydrogen Fuel Cell Stack
The structure of the fuel cell is similar to a battery. The hydrogen enters the anode where it comes in contact with a catalyst, which is usually platinum. This catalyst promotes the separation of hydrogen atoms into a hydrogen ion and an electron.
The hydrogen then passes through an electrolyte membrane to reach the cathode while the electron travels through the circuit, producing electricity to power the motor. At the end of the circuit, the electrons combine with the hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water as a byproduct.
How Is Hydrogen Gas Produced?
Hydrogen gas doesn’t naturally exist in the environment. Therefore, it needs to be produced with man-made methods. The two most common hydrogen production methods are steam-methane reforming and electrolysis.
Steam-Methane Reforming
This is the most commonly used method to produce hydrogen as it is low-cost and easy to do at scale. In steam-methane reforming, pressurized, high-temperature steam (700 to 980 degrees Celsius) reacts with methane in the presence of a catalyst to produce hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and a small amount of carbon dioxide.
The methane used in this process mostly comes from fossil fuel natural gas, and only a small amount of it comes from biogas or renewable natural gas. Since this process produces greenhouse gasses, it’s also not environmentally friendly.
Read More: Everything You need to know about Hybrid Cars
Electrolysis
This process uses electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen gases. You probably remember this experiment from your high school science class. The only components required in this process are water, electricity, and a catalyst. However, that doesn’t mean this method is environmentally friendly as most electrolysis processes still use energy from coal plants. To get a truly “green” hydrogen production method, hydrolysis needs to be done with renewable energy.
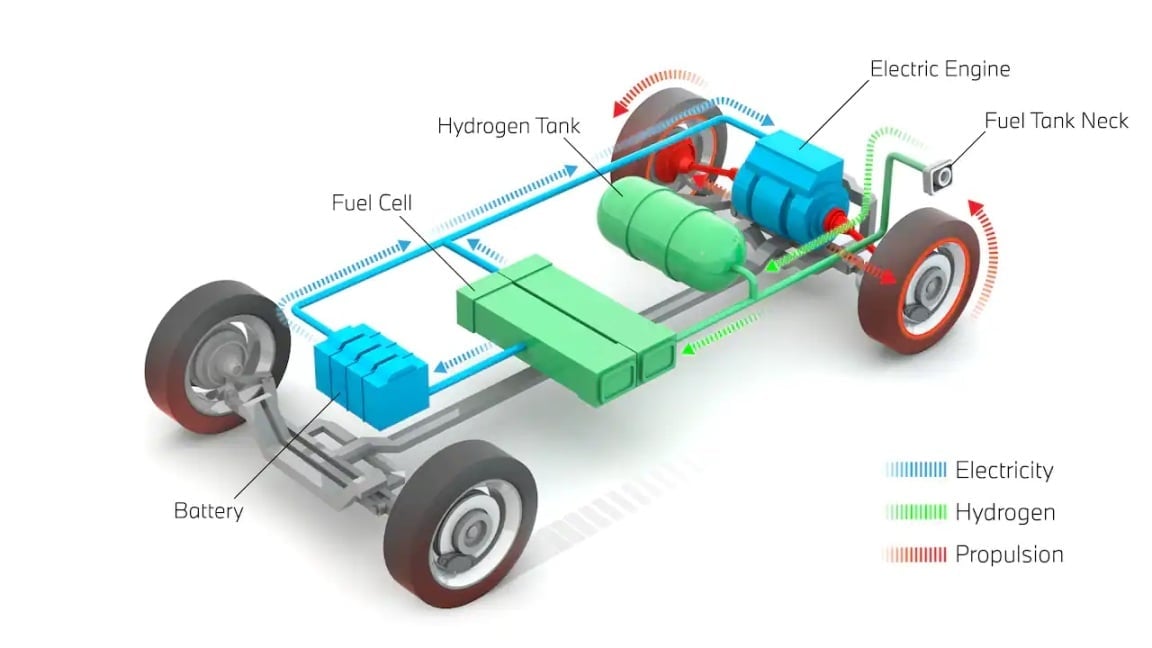
How a hydrogen car is powered [Image source: BMW]
Main Components of a Hydrogen Car
- Battery pack: Similar to full EVs, hydrogen cars have a lithium-ion battery pack that stores electricity to power the motor. However, it typically contains fewer lithium-ion cells and a lower voltage than a BEV battery pack since most of the power comes from the hydrogen fuel cell. This battery pack can be recharged via regenerative braking or with excess electricity from the fuel cell.
- Hydrogen fuel tank: This tank stores hydrogen gas in a highly pressurized environment until it’s needed by the fuel cell. Passenger hydrogen cars typically hold around 5kg of hydrogen gas in their tanks.
- Fuel Cell Stack: This is where hydrogen and oxygen gases are used to generate electricity. The fuel cell contains membrane electrodes where reverse electrolysis occurs, which combines hydrogen and oxygen, producing electricity and water as a byproduct.
- Fuel tank neck: This is the receptacle where you pump hydrogen gas from a gas station into. Unlike in a traditional petrol car, the hydrogen gas pump nozzle needs to stay locked onto the fuel tank neck while refueling as you’re dealing with pressurized gas.
- Electric motor: It uses power from the fuel cell and battery pack to drive the vehicle’s wheels. The motor in a hydrogen car works very much the same way as one in a BEV or hybrid car.
- Thermal cooling system: Similar to a cooling system in a BEV, it cools the fuel cell, electric motor, power control unit, and other components, maintaining an optimal operating temperature for all the components.
- Power control unit: It manages the flow of electrical energy provided by the fuel cell and battery pack to control the speed and torque of the car.
- DC/DC converter: It converts the high voltage DC power from the lithium-ion battery pack and fuel cell to low-voltage DC power to recharge the auxiliary battery and power other vehicle electronics.
- Exhaust pipe: After the chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen produces electricity and water, the water is expelled from the vehicle via the exhaust pipe.
Read More: Do Engine Oil Treatment & Fuel Additives Really Work?
Advantages of Hydrogen Cars
Long Driving Range
The most attractive advantage of hydrogen cars is their longer range when compared to BEVs. Hydrogen cars can generally travel around 600km before needing refueling while the average EV can only travel between 300 to 400km before needing to be recharged.
Produces Zero Emissions
A hydrogen car produces no greenhouse gases. Instead, it only produces water as a byproduct which either gets expelled out of the car as you drive or gets stored in a tank that you can empty yourself.
Quick Refueling
Refueling a hydrogen car is similar to a traditional car. All you need to do is drive up to a hydrogen gas station, connect the hose to your car, and wait for your tank to fill up. This only takes around five minutes compared to recharging a BEV which can take up to a few hours.

Image source: Toyota
Hydrogen Fuel Cells are Lightweight
A hydrogen car fuel cell is generally more lightweight than a lithium-ion battery pack. It also occupies less space and has a greater energy storage density. Because of this, many experts and companies consider hydrogen to be a better option for commercial vehicles, especially large, long-haul trucks.
A fully battery-powered commercial truck would require a large number of battery packs making it significantly heavier than diesel trucks. Hydrogen fuel cells can provide clean energy without bumping up the weight of these trucks.
Disadvantages of Hydrogen Cars
Prices are Expensive
At the moment, hydrogen cars are still very expensive, especially compared to most ICE cars. For instance, the Toyota Mirai costs around $50,000 in the USA while the Toyota Corolla starts at only $20,000. Additionally, refueling hydrogen cars is also costly with a kilogram of hydrogen gas costing on average $15 (RM68) at the pump. With the Mirai being able to travel around 600km on 5.6kg of hydrogen, that means that you would need RM380 worth of hydrogen to drive that distance.
Limited Refueling Stations
There are very limited hydrogen refueling stations even in markets where hydrogen cars are sold. Therefore, hydrogen car owners may find it difficult to refuel their cars. As of 2022, the USA has only 107 hydrogen refueling stations while Japan has 166 stations.
Safety Concerns over Hydrogen Tanks
Many people are still concerned about the safety of storing this highly flammable gas in their cars. However, all hydrogen cars have to satisfy strict safety requirements to ensure that accidents do not happen. Manufacturers such as Toyota pack their hydrogen tanks with advanced safety features including using a tough carbon fiber-reinforced plastic layer to hold the gas in.
There are also failsafes to ensure the hydrogen is safely released into the atmosphere if, for example, the fuel cell overheats or if the car is involved in an accident.
Environmental Impact of Hydrogen Production
While hydrogen cars are clean, the bulk of the hydrogen used globally is produced from natural gas with processes that result in greenhouse gases. That said, many governments and energy companies are finding ways to produce green hydrogen using sustainable methods including extracting it from water (electrolysis) using renewable energy.
In fact, even Malaysia is in on the action as Sarawak is set to be a green hydrogen production and export hub. Some of the hydrogen will even be used to power autonomous rapid transit vehicles in the state.
Read More: 5 Habits That Are Actually Damaging Your Car’s Transmission
Top Hydrogen Cars
Although hydrogen fuel cell technology hasn’t been widely used in passenger cars, there have been quite a number of hydrogen vehicles produced over the years. Here are vehicles that are either available or in development.
Toyota Mirai

The Toyota Mirai was first manufactured in 2014 and is arguably the most well-known hydrogen car in the world. It’s mainly sold in Japan, the USA, Canada, and some parts of Europe. The Mirai has a 142.2L Toyota Fuel Cell System with a 170kW electric power output. This power is delivered to the electric motor which produces 182PS of power and 406.7Nm of torque giving the Mirai a century sprint of 0 to 100 km/h time of 9.2 seconds.
It also has three hydrogen fuel tanks, with a total capacity of 5.6kg giving it a maximum range of 646km on a full charge. While these figures look impressive, the Mirai is priced starting from $49,500 (RM225,398) in the USA, making it too expensive for most consumers.
Hyundai Nexo
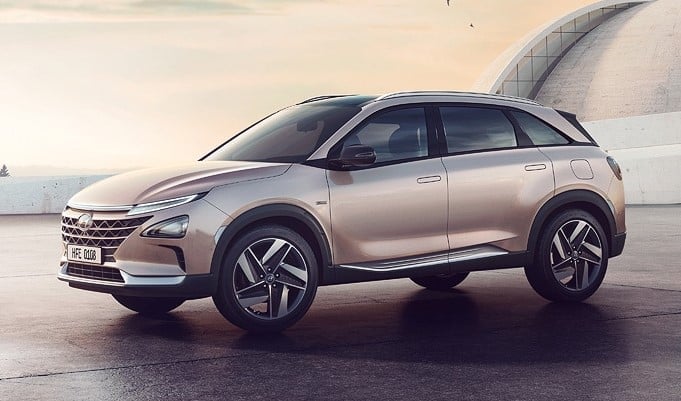

The Hyundai Nexo is a hydrogen fuel cell SUV first introduced in 2018 and is currently available in South Korea, the USA, the UK, and Australia. It has 163.2PS of power and 395Nm of torque making it a very capable vehicle. Its driving range varies from 569km to 611km depending on the variant you choose. Considering that the Nexo has a curb weight of around 1,700kg, its range is impressive indeed. The price of the Hyundai Nexo starts at $59,435 (RM270,577) in the USA.
Renault Master Van H2-Tech

Renault has a sizeable selection of light electric commercial vehicles and started producing hydrogen commercial vans in 2019. At the World Hydrogen Summit and Exhibition 2022, they introduced the Renault Master Van H2-Tech which adds a hydrogen drivetrain to their existing battery-powered Master ZE van.
The Master Van H2-Tech has the same 33kWh battery and 76PS electric motor as its battery-powered cousin, with the addition of a 30kW fuel cell and four 1.5kg hydrogen tanks. The new van boasts a range of up to 500km compared to less than 160km in the Master ZE. The hydrogen drivetrain is placed on the van’s roof, which allows for a low loading height for cargo of up to 12 cubic meters in volume.
Hyperion XP-1

The Hyperion XP-1 is a hypercar 10 years in the making, and yes, it’s powered by hydrogen. Not much technical information is available on the XP-1 other than that it has a lightweight titanium carbon monocoque frame, a compact high-capacity hydrogen storage system using space flight technology, and an all-wheel drive powertrain. It boasts a 1,600km driving range on a single charge, a century sprint time of 2.2 seconds, and a top speed of 354 km/h.
The XP-1’s main advantages over battery electric performance cars are its low-weight hydrogen drivetrain. It has a curb weight of only 1,274kg, less than a McLaren 720s’ 1,467kg. For comparison, Tesla’s flagship Model S Plaid weighs 2,160kg with around 500kg of that being its battery pack, while only having a range of 640km. The XP-1 is scheduled to go into production in 2022 or 2023 and shows a promising future for hydrogen cars.
Hyundai N Vision 74

The Hyundai N Vision 74 is an experimental hydrogen sports car, also referred to as a rolling lab by Hyundai. It uses both hydrogen and a 62.4kWh battery pack to power its dual electric traction motor. Both motors are fitted on the rear axle and together, they produce 670PS of power and 900Nm of torque.
Hyundai’s mission with the N Vision 74 is to develop a hydrogen performance car with an optimized cooling system that ensures performance in heavy track use. To achieve this, they use individual cooling systems for each fuel cell stack, battery, and power electric module. Performance-wise, this hydrogen car can reach speeds of over 250 km/h and travel over 600km on a single charge.
Will Hydrogen Cars Replace Battery Electric Cars?
While hydrogen-powered cars show some potential in being a viable option for us, hydrogen cars and gas refueling are still prohibitively expensive for most consumers. Due to the rapid advancements in the BEV sector, BEVs are also years ahead of their hydrogen counterparts.
That said, several companies such as Toyota and Hyundai along with hydrogen manufacturers and governments are paving the way to improve hydrogen technology. At least for now, the advantages of hydrogen work better for larger commercial vehicles compared to passenger cars. This means that hydrogen FCEVs can exist alongside BEVs albeit in different vehicle segments.
Plus, most countries, including Malaysia, already have some level of EV recharging infrastructure. That’s why it’s unlikely that we’ll see hydrogen passenger cars here any time soon. That being said, we don’t know what the future holds, so never say never!
